atella tendon is a significant structure that enables you to walk, jump, and move without pain. Patella tendon is the structure that holds the kneecap (patella) attached to the shinbone (tibia) and acts as a bridge where the quadriceps push and produce leg movement. Your lifestyle and mobility will be seriously impacted if the big tendon gets injured or ruptured.
What is a Patella Tendon Tear?
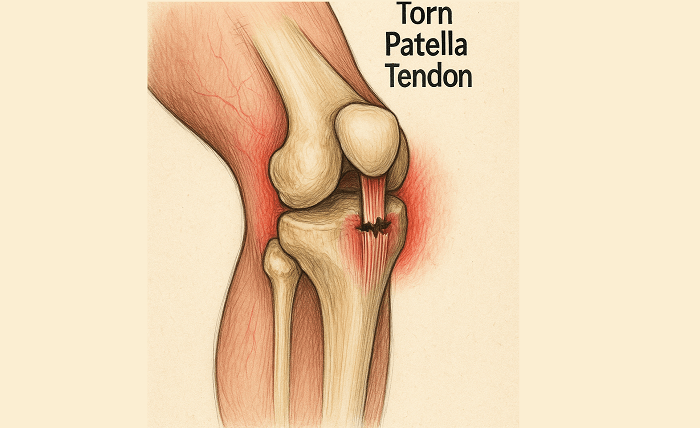
This medical concern is a clinical condition with partial or total rupture of the patella tendon. The patient is more prone to injury in exercise that subjects the knee to high stress, leading to overstretching of tendon fibres or total rupture. Total rupture of the tendon dissociates the tendon from the shinbone or kneecap and renders the knee unstable – the patient cannot typically even straighten the leg.
The symptoms may be severe with sudden pain, swelling, bruising, and the leg may not hold much weight without discomfort. The knee will also become deformed with the kneecap in an elevated position, which is an indication of a complete tear.
Common Causes of Patella Tendon Tears
Patella tendon rupture is expected to occur with stress-loaded movement or with knee injury. The most common instances resulting in an occurrence such as that are as illustrated below.
Sports Injury
Athletes who play contact sports like soccer, football, or basketball will likely overstrain their patella tendons. The tendon is strained through jumping, landing, or direction change and is therefore bound to get injured. For example, the weakening of the tendon due to the continuous jumping of a basketball player makes it vulnerable to straining as it meets with a forceful sudden movement.
Falls or Direct Trauma
Direct blow to the knee or anterior blow to the knee may cause patella tendon injury. This would be most likely due to traumas, i.e., falling on the ground because the ground was slippery or a car crash. Sudden rupture can occur when force is adequate.
Overuse and Chronic Stress
Continued stressing of the knee over a prolonged period will ultimately result in micro-tears along the patella tendon, or patellar tendinopathy or “jumper’s knee.” Micro-tears weaken the strength of the tendon and put the tendon at risk for complete rupture with high-level activity unless intervention is undertaken.
Factors That Contribute to Patella Injury
Although Melbourne’s most experienced knee surgeons see people of all ages and conditions, there are certain factors predisposing one to injury. If you are aware of them, you can be more informed.
Age: Middle-aged women and men, particularly highly active women and men, are more susceptible. Tendons lose their elasticity and get stiff with age.
Pre-Existing Conditions: Certain conditions such as diabetes, rheumatoid arthritis, or chronic renal disease have been discovered to weaken and predispose tendons to rupture.
Use of Corticosteroids: Frequent use of corticosteroid medication over a long period of time has the effect of weakening and losing elasticity in tendons, and thereby raising the risk of injury.
Previous Injury: Individuals with a history of prior knee injury are susceptible to developing further patella tendon rupture.
Deconditioning: Individuals with sedentary lives or those who begin exercising without conditioning will overwork their tendons and hence get hurt.
Healthy Knees
The patella tendon is a major part of knee movement and stability, and knowledge concerning causality of the tear and causative factors are all important within the preventive process. Being an athlete or not being an athlete, simply living life normally with healthy and flexible knee tendons, can lower your risk of injury.
If you have knee pain or a tendency to have patella tendon rupture, go to a physician in time. Early diagnosis and treatment will also be helpful to your recovery.